What is Sugarcane juice?
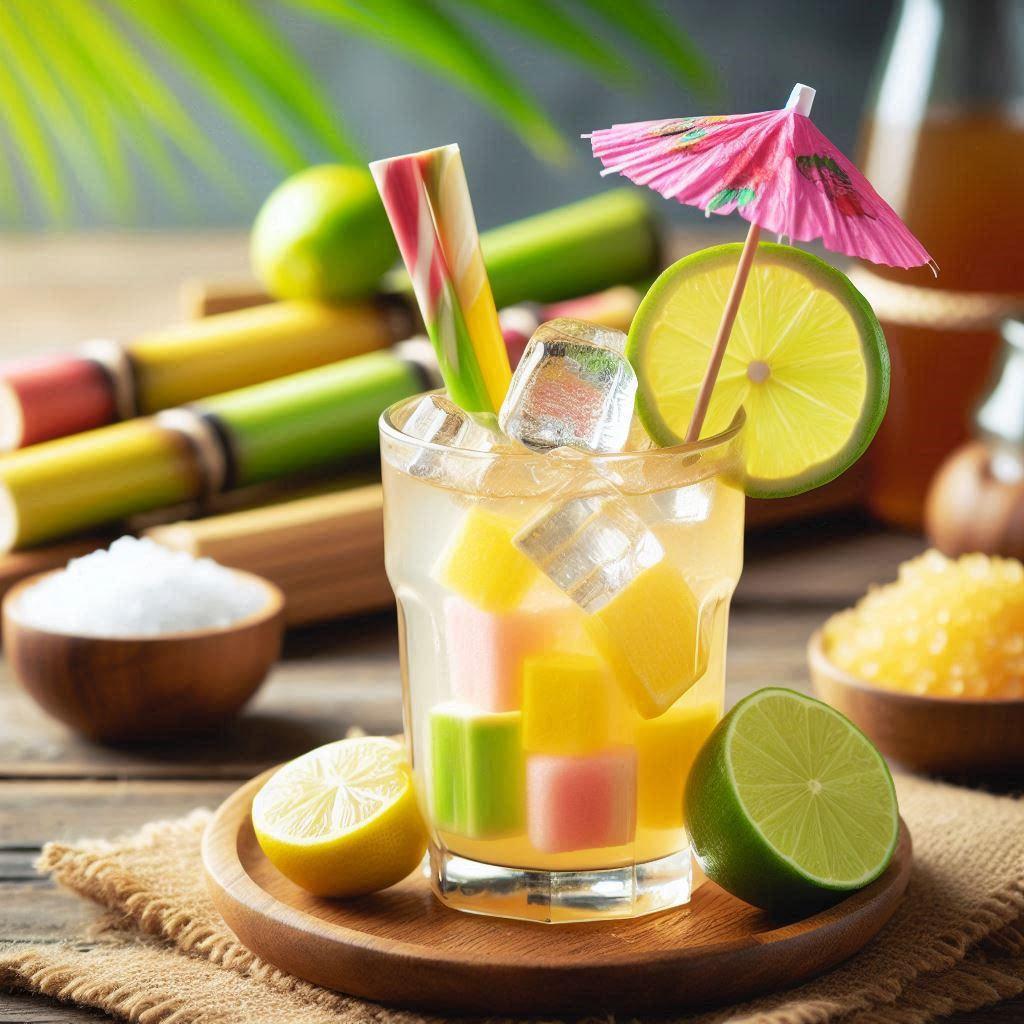

Sugarcane juice is a natural beverage made by extracting the liquid from sugarcane stalks. The process involves crushing or pressing the stalks to release the sweet juice, which is then often filtered and sometimes slightly heated. This juice has a rich, sweet flavor and is typically consumed fresh.
It’s popular in many parts of the world, especially in tropical regions where sugarcane is grown. The juice can be enjoyed on its own or used as a base for cocktails and other drinks. It’s also sometimes boiled down to make a syrup or used in cooking and baking.
Besides its great taste, sugarcane juice is known for its nutritional benefits, including vitamins and minerals like iron, calcium, and magnesium. However, because it’s high in natural sugars, it should be consumed in moderation.
History & origin
Sugarcane juice traces back to ancient times in Southeast Asia, particularly New Guinea, where sugarcane was first cultivated around 8,000 years ago. The juice extraction process was refined in India, where it was used to make jaggery. As sugarcane cultivation spread, notably through Alexander the Great’s conquests, the knowledge of processing sugarcane expanded to the Middle East and Europe. By the medieval period, sugarcane juice and its derivatives had become significant in various cultures, leading to the global popularity of sugarcane juice we see today.
Cultivation & harvesting
Sugarcane is a tropical and subtropical crop, thriving in warm climates with plenty of sunlight and rainfall. Here’s a general overview of its cultivation:
1. Climate and Soil:

- Climate: Sugarcane requires a warm climate with temperatures ranging between 20°C and 30°C (68°F to 86°F). It also needs ample rainfall, though it can be grown in areas with irrigation.
- Soil: It grows best in well-drained, loamy soils rich in organic matter. The soil should be fertile, with a pH between 5.5 and 8.0.
2. Propagation:
- Planting Material: Sugarcane is propagated using stem cuttings, or “setts,” which are sections of mature cane stalks. Each sett typically contains at least one bud.
- Planting: Setts are planted in furrows or trenches. They are covered with soil and require consistent moisture to encourage sprouting.
3. Growth:
- Germination: After planting, the setts take a few weeks to sprout. Initial growth is slow, but once established, sugarcane grows rapidly.
- Development: The plant reaches maturity in 10 to 24 months, depending on the variety and climate. During this period, it develops tall stalks with high sugar content.
4. Care and Maintenance:
- Watering: Regular irrigation is crucial, especially during dry periods. But in order to avoid root rot, avoid overwatering.
- Fertilization: Sugarcane benefits from a balanced fertilizer regimen, including nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, along with occasional micronutrient supplements.
- Weed and Pest Control: Weeds and pests can affect sugarcane yields. Integrated pest management practices and weed control measures are often employed.
5. Harvesting:
- Timing: Sugarcane is harvested when the stalks reach their maximum sugar content, typically after 10 to 24 months. The timing varies based on the variety and climate.
- Method: Harvesting is done either manually using machetes or mechanically with specialized harvesters. The entire stalk is cut close to the ground.
6. Post-Harvest Processing:
- Extraction: Once harvested, sugarcane stalks are crushed to extract the juice, which is then processed to produce sugar or consumed fresh as sugarcane juice.
- Processing: The juice can be boiled down to create syrup or crystallized into sugar.
7. Sustainability and Challenges:
- Sustainability: Sugarcane farming can have environmental impacts, including deforestation and water usage. Sustainable practices, such as crop rotation and efficient water management, are essential.
- Challenges: Sugarcane cultivation faces challenges like pests, diseases, and climate change, which can affect yields and quality.
Sugarcane cultivation is a significant agricultural activity in many tropical and subtropical countries, including Brazil, India, China, and Australia. It plays a crucial role in local economies and global sugar production.
Processing
Processing sugarcane involves several key steps to extract and refine the juice into various products:
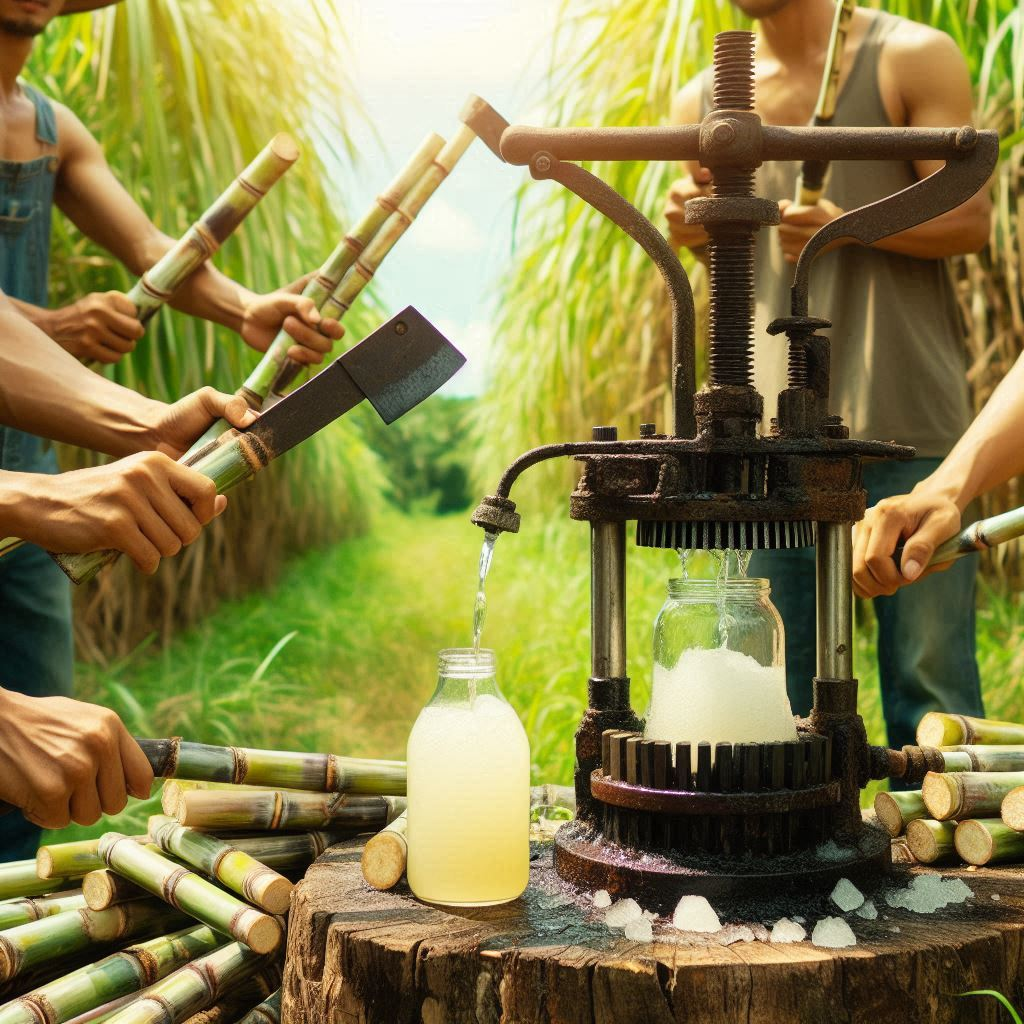

1. Harvesting:
- Cutting: Sugarcane stalks are harvested by hand or machine and transported to processing facilities.
2. Extraction:
- Crushing: The harvested stalks are washed and then crushed using mechanical mills to extract the juice. This juice is then filtered to remove impurities.
3. Clarification:
- Purification: The juice is heated and treated with lime or other clarifying agents to remove suspended particles and impurities.
4. Evaporation:
- Concentration: The clarified juice is boiled in evaporators to reduce its water content, concentrating the juice into a thick syrup.
5. Crystallization (for sugar):
- Cooling: The syrup is further boiled in vacuum pans to crystallize the sugar.
- Centrifugation: The mixture is spun in a centrifuge to separate the sugar crystals from the remaining liquid, known as molasses.
6. Drying:
- Processing: The separated sugar crystals are dried and then refined to remove any remaining molasses, resulting in white or brown sugar.
7. Further Processing (for other products):
- Syrup: The thick syrup can be further processed into products like molasses or used as a sweetener.
- Sugarcane Juice: If consumed fresh, the juice can be chilled and served immediately or pasteurized for longer shelf life.
Recipe
Here are a few recipes using sugarcane juice:
1. Classic Sugarcane Juice:
Ingredients:
- Fresh sugarcane stalks
- Water (if needed)
- Lemon or lime juice (optional)
- Mint leaves (optional)
- Ice cubes (optional)
Instructions:

- Prepare Sugarcane: Wash and peel the sugarcane stalks. Cut them into smaller sections.
- Extract Juice: Using a sugarcane juicer or a manual press, extract the juice from the sugarcane sections.
- Filter: Strain the juice through a fine sieve to remove any fibrous particles.
- Flavor: Add lemon or lime juice for a tangy flavor. For a cool variation, you can also incorporate mint leaves.
- Serve: Chill the juice with ice cubes or serve immediately.
2. Sugarcane Juice Lemonade:
Ingredients:
- 1 cup fresh sugarcane juice
- 1/4 cup freshly squeezed lemon juice
- Two teaspoons of sugar or honey (optional; taste and adjust)
- 1 cup cold water or sparkling water
- Ice cubes
- Lemon slices and mint leaves for garnish
Instructions:
- Mix: In a pitcher, combine the sugarcane juice and lemon juice. Stir well.
- Sweeten: Add honey or sugar if desired, and stir until dissolved.
- Dilute: Add cold water or sparkling water to the mixture.
- Chill: Add ice cubes and chill before serving.
- Garnish: Serve with lemon slices and mint leaves.
3. Sugarcane Juice Smoothie:
Ingredients:
- 1 cup fresh sugarcane juice
- 1 banana
- 1/2 cup Greek yogurt or milk
- Half a cup of frozen berries, such as blueberries, raspberries, or strawberries
- 1 tablespoon honey or agave syrup (optional)
- Ice cubes
Instructions:
- Blend: In a blender, combine sugarcane juice, banana, Greek yogurt, frozen berries, and honey.
- Process: Blend until smooth and creamy.
- Adjust: Add ice cubes and blend again if a thicker consistency is desired.
- Serve: Pour into glasses and enjoy immediately.
4. Sugarcane Juice Mojito (Non-Alcoholic):
Ingredients:
- 1 cup fresh sugarcane juice
- Juice of 1 lime
- 1/2 cup mint leaves
- 1-2 tablespoons honey or sugar (optional)
- Sparkling water
- Ice cubes
- Lime wedges and mint sprigs for garnish
Instructions:
- Muddle: In a glass, muddle the mint leaves with lime juice and honey or sugar.
- Mix: Add sugarcane juice and stir to combine.
- Top: Fill the glass with ice cubes and top with sparkling water.
- Garnish: Garnish with lime wedges and mint sprigs.
Nutritional composition
Sugarcane juice is rich in several nutrients but also high in natural sugars. Its nutritional composition generally includes:
1. Carbohydrates:
- Sugars: Predominantly sucrose, glucose, and fructose. It provides a quick source of energy.
2. Vitamins:
- Vitamin C: Offers antioxidant benefits and supports immune function.
- B Vitamins: Includes small amounts of vitamins such as B1 (thiamine), B2 (riboflavin), and B6 (pyridoxine).
3. Minerals:
- Iron: Important for blood health.
- Calcium: Supports bone health.
- Magnesium: Contributes to muscle and nerve function.
- Potassium: Helps regulate blood pressure and fluid balance.
4. Antioxidants:
- Polyphenols: Help combat oxidative stress and inflammation.
5. Other Compounds:
- Amino Acids: Present in small amounts, contributing to overall protein content.
Benefits
Sugarcane juice offers several health benefits:
1. Hydration:
- Replenishing: Provides hydration and replenishes electrolytes, especially beneficial after exercise or in hot climates.
2. Nutrient-Rich:
- Vitamins and Minerals: Supplies essential nutrients like vitamin C, iron, calcium, and magnesium, supporting overall health.
3. Antioxidant Properties:
- Combat Oxidative Stress: Contains antioxidants that help neutralize free radicals and reduce inflammation.
4. Digestive Health:
- Supports Digestion: Contains dietary fiber and can help improve digestive health and alleviate constipation.
5. Energy Boost:
- Quick Energy Source: The natural sugars provide a quick energy boost and can help alleviate fatigue.
6. Skin Health:
- Anti-Aging: Vitamin C and antioxidants may support skin health and reduce signs of aging.
Disadvantages
While sugarcane juice has benefits, it also has some disadvantages:
1. High Sugar Content:
- Caloric Intake: High in natural sugars, which can contribute to weight gain and increase the risk of diabetes if consumed excessively.
2. Dental Health:
- Tooth Decay: The sugars can promote tooth decay and cavities if oral hygiene is not maintained.
3. Blood Sugar Spikes:
- Glycemic Impact: Can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels, particularly problematic for people with diabetes.
4. Limited Shelf Life:
- Perishability: Fresh juice spoils quickly and often requires refrigeration or preservatives to extend its shelf life.
5. Nutritional Imbalance:
- Low in Protein and Fat: Lacks significant amounts of protein and fat, which are essential for a balanced diet.
Culinary Uses and Variations
Sugarcane juice’s versatility extends beyond being a standalone beverage. It can be used in various culinary applications:
- Flavoring Agent: It can be used as a natural sweetener in smoothies, cocktails, and even desserts, providing a unique flavor and natural sweetness.
- Ice Cream and Sorbet: Sugarcane juice can be turned into refreshing ice creams and sorbets, adding a tropical twist to frozen treats.
- Marinades and Sauces: The juice can be incorporated into marinades and sauces, enhancing their flavor profile with its natural sweetness.
- Cocktails: In mixology, sugarcane juice serves as a base for creative cocktails, offering a tropical flair to beverages.
Cultural Significance
Sugarcane juice holds a special place in the cultural traditions of various countries:
- India: In India, sugarcane juice, known as “Ganna Juice,” is a popular street drink enjoyed throughout the country. It is often served with a squeeze of lime and a pinch of salt, making it a refreshing choice in the sweltering heat.
- Brazil: In Brazil, sugarcane juice is known as “Caldo de Cana” and is a staple in many regions. It is commonly served with snacks and is a traditional part of Brazilian cuisine.
- Caribbean: In the Caribbean, sugarcane juice is enjoyed as a refreshing beverage and is often flavored with additional ingredients like ginger or lime.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ’s)
1. Is sugarcane juice healthy?
- Yes, it contains essential nutrients and antioxidants but is high in natural sugars. Moderation is important.
2. Can sugarcane juice help with digestion?
- Yes, it can aid digestion and relieve constipation due to its fiber content.
3. How should sugarcane juice be stored?
- Fresh juice should be refrigerated and consumed within a few days to prevent spoilage. It can also be pasteurized for longer shelf life.
4. Does sugarcane juice contain caffeine?
- No, it does not contain caffeine.
5. Can sugarcane juice be consumed by people with diabetes?
- People with diabetes should consume it in moderation due to its high sugar content and consult with a healthcare provider.
6. Is sugarcane juice good for skin health?
- Its vitamin C and antioxidants can support skin health and have anti-aging benefits.
7. How can I use sugarcane juice in recipes?
- It can be enjoyed as a beverage, used in cocktails, or as a sweetener in cooking and baking.
Conclusion
Sugarcane juice is a delightful and nutritious beverage that combines natural sweetness with a host of health benefits. Its rich nutritional profile, versatility in culinary applications, and cultural significance make it a standout choice in the world of natural drinks. Whether you’re looking to stay hydrated, boost your energy, or simply enjoy a refreshing treat, sugarcane juice offers a delicious and healthful option. So, the next time you’re in search of a natural elixir, consider indulging in the sweet and revitalizing goodness of sugarcane juice – a true gift from nature.
Table of Contents
Read more about Sugarcane juice
Go and visit dusearchit.in and get more knowledge about others topics.
