Introduction
Ghee(clarified butter), often referred to as clarified butter, is a cornerstone of traditional Indian cuisine and a beloved ingredient in many other culinary traditions around the world. Its rich, nutty flavor and high smoke point make it a versatile cooking fat, but its benefits extend far beyond the kitchen. This comprehensive guide will delve into the origins, preparation methods, nutritional benefits, and potential drawbacks of ghee, highlighting why this golden elixir has earned its place in modern diets.
What is Ghee?
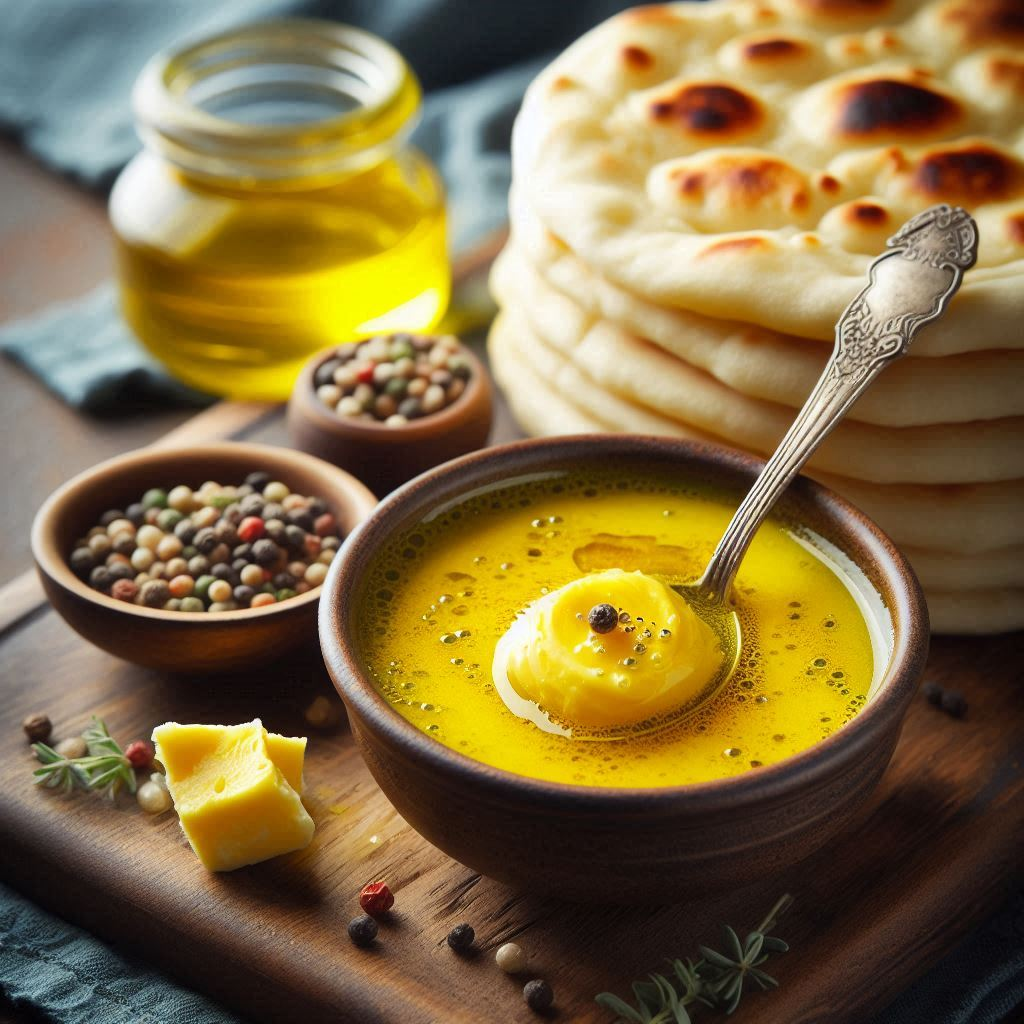

Ghee is essentially clarified butter. The process of making ghee involves simmering butter to remove its water content and milk solids, leaving behind pure butterfat. The result is a golden, aromatic fat with a high smoke point—around 450°F (232°C)—which makes it ideal for cooking at high temperatures. Unlike regular butter, ghee is free of lactose and casein, making it a suitable option for those with dairy sensitivities.
Historical Origins
- Ancient Texts and Traditions:
- Vedic Period (1500–500 BCE): Clarified butter is mentioned in the Vedas, the ancient sacred texts of Hinduism. In these texts, it was used in rituals and sacrifices, symbolizing purity and divine essence.
- Ayurveda: Clarified butter is also a key component in Ayurveda, the traditional Indian system of medicine. It is valued for its medicinal properties and is believed to enhance digestion, boost immunity, and promote longevity.
- Cultural Significance:
- Hindu Rituals: In Hindu culture, Clarified butter has been used for thousands of years in religious ceremonies and offerings. It is considered sacred and is often used in lamps and as a base for various ceremonial foods.
- Dietary Use: In traditional Indian cuisine, Clarified butter has been a staple due to its flavor, high smoke point, and preservation qualities. Unlike regular butter, ghee is made by simmering butter to remove water and milk solids, which gives it a longer shelf life.
- Spread to Other Regions:
- Middle Eastern Influence: Clarified butter preparation and use spread to the Middle East through trade and cultural exchange. It influenced the cuisines of countries like Iran and Afghanistan, where it is known as “roghan” or “khiar.”
- Global Popularity: In recent decades, Clarified butter has gained popularity beyond South Asia due to its health benefits and unique flavor, leading to its incorporation into various global culinary traditions.
Production Process
- Making Ghee:
- Clarification: To make Clarified butter, butter is melted and simmered until the milk solids separate from the fat and settle at the bottom. The clear, golden fat is then strained, leaving behind the impurities.
- Storage: Clarified butter has a high smoke point, which makes it suitable for frying and cooking at high temperatures. It can be stored at room temperature for extended periods without spoiling.
- Nutritional Benefits:
- Nutrients: Clarified butter is rich in essential fatty acids, vitamins A, D, E, and K, and antioxidants. It is also believed to be easier to digest than regular butter because the milk solids are removed.
How to Make Ghee

Making gheee at home is relatively simple, though it requires patience. Here’s a basic recipe:
- Start with Unsalted Butter: Use high-quality, unsalted butter, preferably organic. The amount can vary, but start with 1-2 pounds for a manageable batch.
- Melt the Butter: Place the butter in a heavy-bottomed saucepan over medium heat. Allow it to melt slowly.
- Simmer and Clarify: Once melted, the butter will start to bubble and foam. Lower the temperature to a gentle simmer. The milk solids will separate and sink to the bottom while the clear golden liquid rises to the top.
- Strain the Ghee: After about 15-20 minutes, the milk solids will turn brown and the bubbling will subside. Carefully strain the clear liquid through a cheesecloth or a fine-mesh strainer into a clean, dry jar. Before sealing, let it cool fully.
- Store Properly: Store ghe in an airtight container at room temperature or in the refrigerator. It can last for several months if stored properly.
Ghe is often praised for its nutritional benefits, especially when compared to other fats and oils. Here’s a breakdown of its nutritional profile and key health benefits:
Culinary Uses
Ghe’s unique flavor profile and cooking properties make it a versatile ingredient in the kitchen:
- Cooking and Baking: Ghe’s high smoke point allows it to be used for frying, sautéing, and roasting without burning. It adds a rich, buttery flavor to dishes and can be used in place of other fats or oils.
- Flavor Enhancer: Use ghe as a finishing touch for vegetables, meats, and grains to add depth and richness to your dishes.
- Traditional Recipes: Ghe is a key ingredient in many traditional Indian recipes, including curries, dals (lentil dishes), and biryanis (rice dishes).
- Spread and Condiment: Ghe can be used as a spread on bread or as a base for sauces and dressings.
Nutritional Composition
- Fat Content:
- Total Fat: Ghe is primarily composed of fat, with about 62-65% fat content.
- Saturated Fat: Approximately 60% of the fat in ghee is saturated fat, including medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs), which are thought to be metabolized more efficiently than other types of fats.
- Vitamins:
- Vitamin A: Ghe is a rich source of vitamin A, which is essential for vision, immune function, and skin health.
- Vitamin D: It contains vitamin D, which supports bone health and immune function.
- Vitamin E: An antioxidant that helps protect cells from damage and supports skin health.
- Vitamin K: necessary for healthy bones and blood coagulation.
- Short-Chain and Medium-Chain Fatty Acids:
- Butyrate: Ghe is a good source of butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid that supports gut health and has anti-inflammatory properties.
- Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA): Ghe contains CLA, which is associated with various health benefits, including improved body composition and anti-cancer properties.
- Other Nutrients:
- Antioxidants: Ghe contains antioxidants that help neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Ghe made from the milk of grass-fed cows may have higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids, which are beneficial for heart health.
Health Benefits

- Digestive Health:
- The butyrate in ghe supports a healthy gut lining and may improve digestion. Its anti-inflammatory qualities may also help with digestive issues.
- Heart Health:
- While ghe is high in saturated fat, it may have a neutral effect on heart health when consumed in moderation, especially if it replaces less healthy fats in the diet.
- Immune Support:
- The vitamins A, D, and E in ghe contribute to a healthy immune system and overall well-being.
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties:
- The butyrate and CLA in ghee may help reduce inflammation in the body, potentially lowering the risk of chronic diseases.
- Skin Health:
- Ghe’s high vitamin A content is beneficial for maintaining healthy skin and may help with skin conditions.
Considerations
- Calories:
- Ghe is calorie-dense, with about 112 calories per tablespoon. Moderation is key, especially for those managing calorie intake.
- Saturated Fat:
- Although ghe contains beneficial fats, its high saturated fat content means it should be consumed in moderation, particularly for individuals with heart disease or cholesterol concerns.
Disadvantages
While ghe has several nutritional benefits, it also has some potential disadvantages that are worth considering, especially depending on individual health needs and dietary goals. Here are some of the important disadvantages of it:
1. High in Calories
- Ghe is calorie-dense, with about 112 calories per tablespoon. Excessive consumption can contribute to weight gain if not balanced with physical activity and overall calorie intake.
2. High in Saturated Fat
- Ghe contains a significant amount of saturated fat (about 60% of its fat content). High intake of saturated fat can be associated with increased levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol, which may raise the risk of heart disease. Moderation is important, especially for individuals with cholesterol or cardiovascular issues.
3. Potential for Allergens
- Although ghe is made by removing milk solids, it may still contain trace amounts of lactose and casein (a milk protein). This could potentially cause issues for individuals with severe lactose intolerance or milk allergies.
4. Cost
- Ghe can be more expensive than other cooking fats, such as vegetable oils or butter, which may be a consideration for some people.
5. High Smoke Point Risks
- While ghe has a high smoke point (around 450°F or 232°C), it can still degrade at very high temperatures or prolonged cooking, potentially forming harmful compounds if overheated.
6. Lack of Essential Fatty Acids
- Ghe is low in omega-3 fatty acids compared to other sources like fish oil or flaxseed oil. Relying too heavily on ghe for dietary fats could result in inadequate intake of these essential fatty acids.
7. Sustainability Concerns
- The production of ghe, especially when sourced from conventionally raised cows, may have environmental implications. Concerns about animal welfare and the environmental impact of dairy farming are considerations for those following a more eco-conscious or plant-based diet.
8. Not Suitable for All Diets
- Ghe may not align with vegan or plant-based diets, and those avoiding animal products would need to choose alternatives like plant-based oils.
Ghee v/s Other Fats
When compared to other cooking fats like olive oil or coconut oil, ghee has some distinct advantages:
- Stability at High Temperatures: Ghee’s high smoke point makes it more stable for high-heat cooking compared to olive oil, which has a lower smoke point.
- Nutrient Profile: Ghee offers a different set of nutrients compared to coconut oil or olive oil, including butyrate and CLA, which can be beneficial for gut health and inflammation.
- Flavor: Ghee imparts a unique, nutty flavor that can enhance dishes in ways that other fats might not.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ’s)
1. What’s ghee?
Ghee is a type of clarified adulation that originates from the Indian key. It’s made by stewing adulation to remove water and milk solids, leaving behind a pure, golden fat.
2. How is ghee different from regular adulation?
Ghee differs from regular adulation in that it has had the milk solids and water removed through a cuisine process. This results in a advanced bank point( around 450 °F or 232 °C) and a richer, nutty flavor. Regular adulation contains these milk solids and has a lower bank point.
3. Is ghee suitable for people with lactose dogmatism?
Ghee is frequently permitted better than regular adulation by people with lactose dogmatism because the milk solids, which contain lactose, are removed. still, it may still contain trace quantities of lactose, so individualities with severe lactose dogmatism should exercise caution.
4. Can ghee be used in cuisine and baking?
Yes, ghee is protean and can be used for cuisine, baking, sautéing, and frying. Its high bank point makes it ideal for high- temperature cuisine.
5. What are the health benefits of ghee?
Ghee is rich in essential adipose acids, vitamins A, D, E, and K, and antioxidants. It’s believed to support digestive health, vulnerable function, and skin health, and may haveanti-inflammatory parcels.
6. Are there any health enterprises associated with ghee?
Ghee is high in calories and impregnated fat. inordinate consumption may contribute to weight gain and increased situations of LDL cholesterol, potentially raising heart complaint threat. temperance is crucial.
7. How should ghee be stored?
Ghee can be stored at room temperature in an watertight vessel for several months, as it has a low humidity content which helps help corruption. It can also be cooled to extend its shelf life.
8. Can ghee be used in vegan diets?
No, ghee is an beast product, so it is n’t suitable for vegan diets. Insectivores generally use factory- grounded canvases like coconut oil painting or olive oil painting as druthers .
9. How can I make ghee at home?
To make ghee at home, poach unsalted adulation in a visage over low heat until the milk solids separate and sink to the bottom, and the liquid turns golden and clear. Strain out the milk solids to gain the ghee.
10. Is ghee the same as clarified adulation?
While ghee and clarified adulation are analogous, they are n’t identical. Clarified adulation is made by melting adulation and removing the milk solids, while ghee is cooked longer, which gives it a distinct nutty flavor and deeper color.
11. Can ghee be used for deep frying?
Yes, ghee’s high bank point makes it suitable for deep frying. still, it’s important to cover the temperature to avoid overheating and implicit declination of the fat.
12. What are the environmental and ethical considerations of using ghee?
The environmental impact of ghee product, particularly from conventionally raised dairy cows, includes enterprises about beast weal and sustainability. concluding for ghee from lawn- fed cows can be a more ethical and sustainable choice.
13. Can ghee be part of a low- carb or ketogenic diet?
Yes, ghee fits well into low- carb and ketogenic diets due to its high fat content and lack of carbohydrates. It’s frequently used in these diets to give healthy fats.
14. How does ghee compare to other cuisine fats like olive oil painting or coconut oil painting?
Ghee has a advanced bank point than olive oil painting and is more stable for high- temperature cuisine compared to coconut oil painting. still, olive oil painting provides a good source of monounsaturated fats and antioxidants, while coconut oil painting offers medium- chain triglycerides( MCTs). The stylish choice depends on individual salutary requirements and cuisine styles.
Conclusion
Ghee is much more than a cooking fat; it’s a versatile ingredient with deep cultural roots and a host of health benefits. Whether you’re looking to enhance your culinary creations or seeking an alternative to other cooking fats, ghee offers a rich, flavorful option that can be both delicious and nutritious. As with any dietary component, balance and moderation are key to maximizing its benefits while minimizing potential drawbacks. So, embrace the golden elixir and discover the many ways ghee can enrich your diet and your life.
Table of Contents
Read more about Ghee
Go and visit dusearchit.in and get more knowledge about others topics.
