What is black raisins?
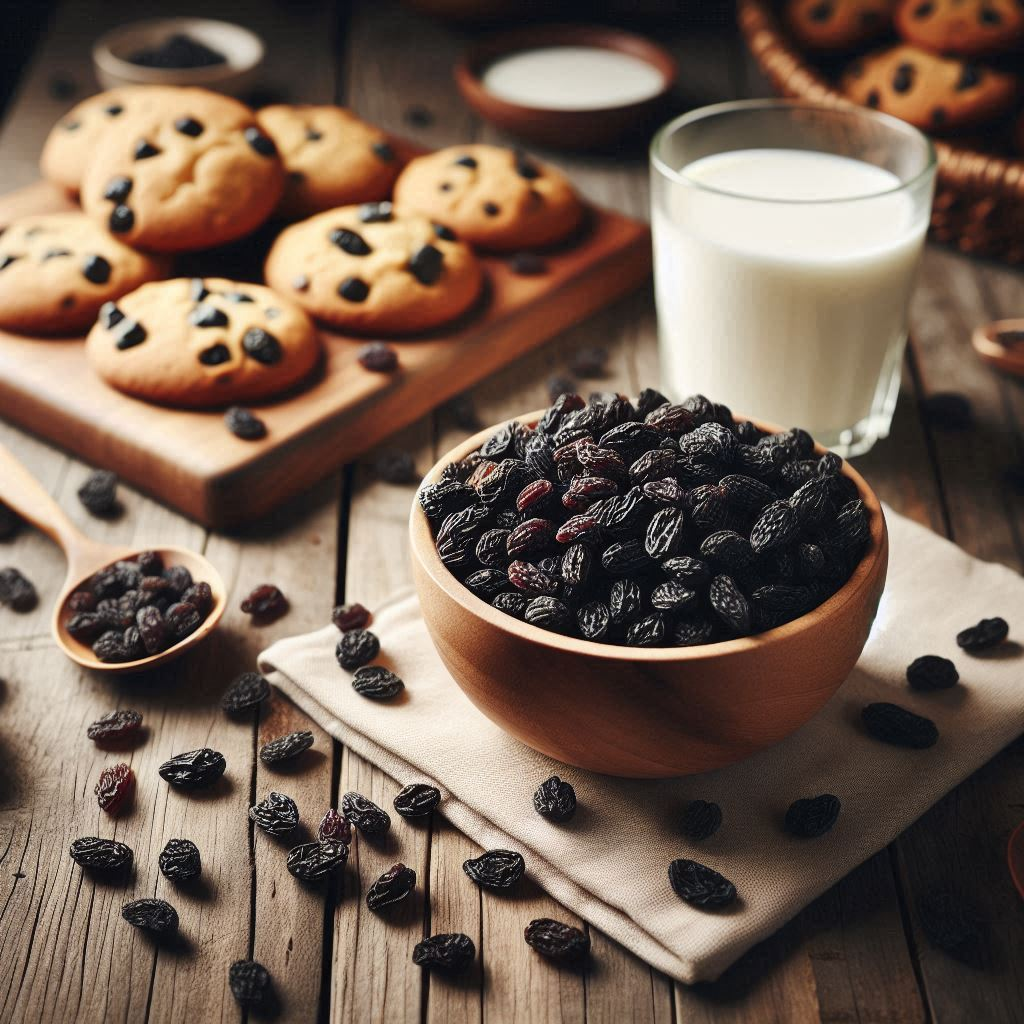

Black raisins are dried grapes that have a dark color, ranging from dark brown to almost black. They are produced by drying grapes, typically of a darker variety, either in the sun or in dehydration facilities.
Raisins in general are sweet and often used in cooking, baking, or as a snack on their own. Black raisins specifically are known for their slightly deeper flavor compared to regular golden raisins, and they are commonly used in various cuisines around the world.
Origin and cultivation
Black raisins, like other types of raisins, are primarily made from grapes that are cultivated specifically for drying. The origins of grape cultivation for raisin production can be traced back thousands of years. Historically, raisins have been an important food source and were valued for their sweetness, portability, and long shelf life.
Origin: Grapes used for making raisins are cultivated in various regions around the world. Some of the major producers include:
- Turkey: Turkey is one of the largest producers of raisins globally, including black raisins. Turkish raisins are known for their quality and are exported to many countries.
- Iran: Iran also has a long history of grape cultivation and is known for producing high-quality raisins, including black raisins.
- United States: California is a significant producer of raisins in the United States. The San Joaquin Valley in California is particularly well-known for its raisin production.
- Greece, Australia, Chile, and South Africa: These countries also cultivate grapes for raisin production, including black raisins, contributing to the global supply.
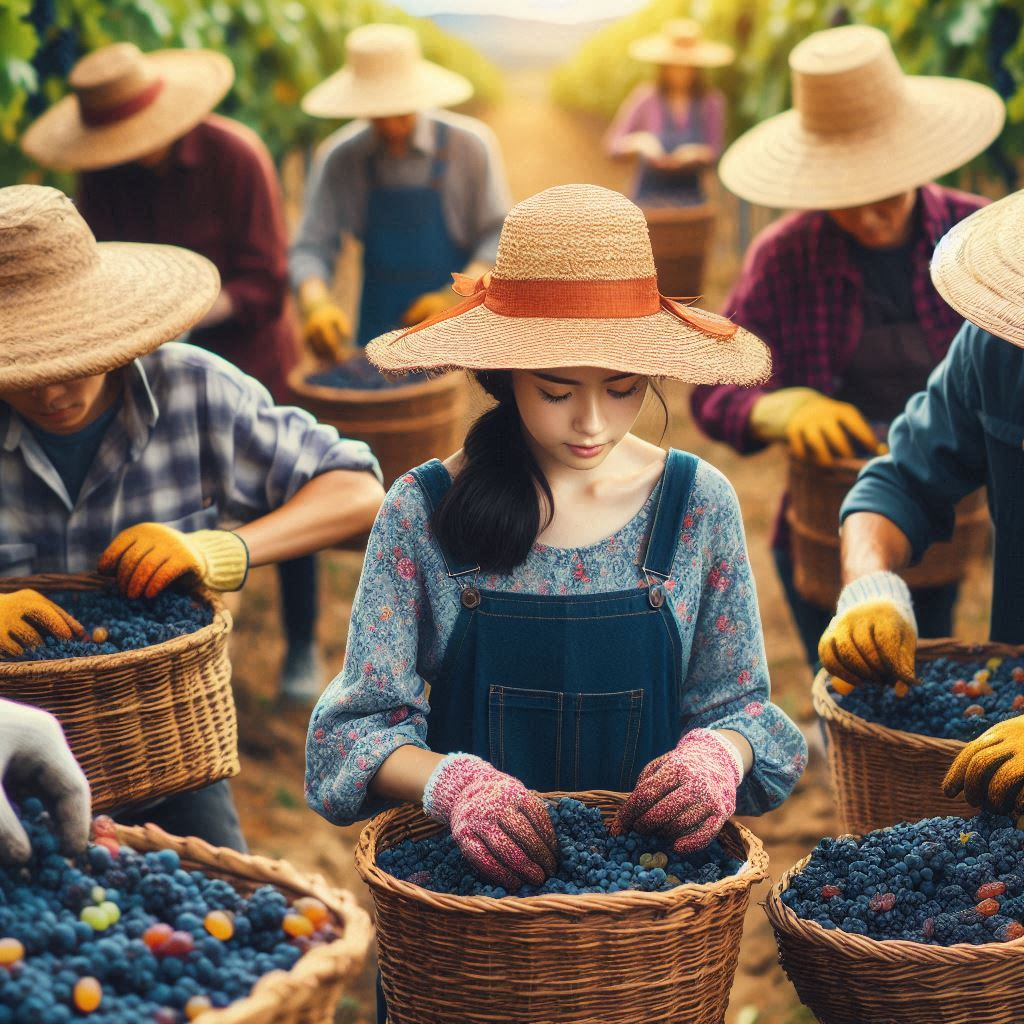

Cultivation: The cultivation of grapes for raisin production involves several stages:
- Grape Varieties: Specific grape varieties are chosen for their suitability for drying into raisins. These varieties often have thick skins and are naturally sweet.
- Growth and Harvesting: Grapes are grown in vineyards under controlled conditions to ensure optimal growth. They are typically harvested in late summer or early autumn when they have reached the desired level of ripeness.
- Drying Process: After harvesting, grapes are laid out to dry. Traditionally, this was done in the sun, but modern methods also include drying in dehydrators or drying tunnels. During the drying process, the grapes lose moisture and concentrate their sugars, becoming raisins.
- Packaging and Distribution: Once dried, the raisins are sorted, cleaned, and packaged for distribution to markets around the world.
Types
There are several types of raisins available, each distinguished by their color, flavor, and production method. Here are some basic types of raisins:
- Black Raisins: Also known as dark raisins, these are dried grapes that have a dark color, ranging from dark brown to almost black. They are often made from grapes such as Black Corinth or Black Muscat.
- Golden Raisins: These raisins are made from green or yellow grapes treated with sulfur dioxide to retain their light color. They are generally plumper and sweeter compared to other types.
- Sultanas: Sultanas are dried seedless grapes that are typically lighter in color than other raisins, often golden brown. They are made from seedless grapes such as Thompson Seedless.
- Currants: Currants are very small dried grapes, often made from the Black Corinth grape variety. They are darker in color and smaller than other raisins.
- Sun-Dried Raisins: These raisins are dried naturally in the sun, without the use of artificial dehydration methods. This traditional method is still used in some regions.
Nutritional composition
The nutritional composition of raisins, including black raisins, varies slightly depending on factors such as size, moisture content, and the specific grape variety used. Here is a general overview of the nutritional composition of raisins per 100 grams:
- Calories: Raisins are relatively high in calories due to their natural sugars and dried nature. They provide about 299 calories per 100 grams.
- Carbohydrates: Raisins are predominantly composed of carbohydrates, primarily natural sugars (fructose and glucose). They typically contain around 79 grams of carbohydrates per 100 grams.
- Fiber: Raisins are a good source of dietary fiber, providing approximately 3.7 grams per 100 grams. Fiber helps promote digestive health and can aid in maintaining healthy cholesterol levels.
- Protein: Raisins contain a small amount of protein, usually around 3 grams per 100 grams.
- Fat: Raisins are very low in fat, with less than 1 gram of fat per 100 grams.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Raisins are rich in certain vitamins and minerals, including:
- Potassium: Important for maintaining healthy blood pressure and heart function.
- Iron: It is important for the production of red blood cells(RBC).
- Calcium: Important for bone health.
- Magnesium: Helps regulate muscle and nerve function.
- Antioxidants: Raisins, especially dark-colored varieties like black raisins, contain antioxidants such as flavonoids and phenolic acids. These compounds help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals.
Culinary uses
Black raisins, like other types of raisins, are versatile in culinary applications and can be used in various dishes to add sweetness, texture, and flavor. Here are some common culinary uses of black raisins:

- Baking: Black raisins are frequently used in baking recipes such as cakes, cookies, breads, muffins, and scones. They add natural sweetness and chewiness to baked goods.
- Trail Mixes and Snacks: Black raisins are a popular ingredient in trail mixes, granola bars, and snack mixes. They provide a natural source of energy and sweetness.
- Salads: Black raisins can be added to salads to complement savory flavors with a touch of sweetness. They pair well with leafy greens, nuts, cheeses, and vinaigrette dressings.
- Rice Dishes: In many cuisines, especially Middle Eastern and Indian, black raisins are used in rice dishes such as pilafs, biryanis, and couscous. They add sweetness and texture to the savory rice preparations.
- Curries and Stews: Black raisins can be added to curries and stews to balance out spicy or savory flavors with their natural sweetness. They are particularly common in Middle Eastern and North African cuisines.
- Chutneys and Sauces: Black raisins are sometimes included in chutneys and sauces, adding a sweet and tangy flavor. They can be used in fruit chutneys, savory sauces for meats, or as a component in marinades.
- Stuffings : Black raisins can be included in stuffings for poultry, game, or vegetables. They adds up sweetness.
- Desserts: Black raisins are used in various desserts such as rice pudding, bread pudding, fruitcakes, and pies. They can be soaked in liquids like rum or brandy to enhance their flavor before adding to desserts.
Benefits
Black raisins offer several health benefits due to their nutrient content and natural compounds. Here are some of the key benefits:
- Rich in Antioxidants: Black raisins contain antioxidants such as flavonoids and phenolic acids. By assisting the body in resisting free radicals, these substances lessen oxidative stress and the chance of developing chronic illnesses.
- Good Source of Fiber: Raisins, including black raisins, are a good source of dietary fiber. Constipation can be avoided and regular bowel movements encouraged by fiber, which benefits gut health. It also supports the maintenance of normal cholesterol levels.
- Natural Energy Boost: Black raisins are naturally high in carbohydrates and sugars, providing a quick energy boost. They are often used by athletes and individuals needing a quick source of energy.
- Rich in Vitamins and Minerals: Raisins contain various vitamins and minerals, including potassium, iron, calcium, magnesium, and vitamin B6. These nutrients play important roles in maintaining overall health, including bone health, blood pressure regulation, and immune function.
- Heart Health: The potassium and dietary fiber in black raisins contribute to heart health. Potassium helps regulate blood pressure, while fiber can help reduce cholesterol levels, both of which are important for cardiovascular health.
- Weight Management: Despite being relatively high in natural sugars, black raisins can still be part of a healthy diet when consumed in moderation. Their fiber content helps promote satiety, which can aid in weight management by reducing overall calorie intake.
- Bone Health: Calcium and boron, which are found in raisins, are necessary for strong bones and the prevention of osteoporosis.
- Supports Skin and Hair Health: The antioxidants in black raisins help protect the skin cells from damage and promote healthy skin. Additionally, the iron and vitamin C content support healthy hair growth and maintenance.
Disadvantages
While black raisins offer several health benefits, there are also some potential disadvantages to consider, particularly when consumed in excessive amounts or for certain individuals:

- High in Natural Sugars: Raisins, including black raisins, are concentrated sources of natural sugars, primarily fructose and glucose. Consuming large quantities can contribute to calorie intake and may affect blood sugar levels, especially for individuals with diabetes or those trying to manage their sugar intake.
- Caloric Density: Raisins are calorie-dense due to their drying process, which removes water and concentrates nutrients and sugars. This can contribute to weight gain if consumed in excess without considering overall calorie intake.
- Potential for Dental Issues: The sticky texture of raisins can adhere to teeth, promoting plaque formation and potentially increasing the risk of dental cavities if oral hygiene is not maintained.
- Sulfites Sensitivity: Some raisins, including black raisins, may contain sulfites as preservatives, which can cause allergic reactions in sensitive individuals.
- Digestive Issues: The high fiber content in raisins can be beneficial for most people, but consuming large amounts may cause digestive discomfort such as bloating or gas, particularly if not accompanied by adequate water intake.
- Potential for Heavy Metal Contamination: There have been occasional concerns about heavy metal contamination in dried fruits, including raisins. Ensuring you purchase from reputable sources and checking for quality assurances can mitigate this risk.
- Impact on Blood Pressure: While potassium in raisins is beneficial for many people, individuals with kidney disease or those taking medications that affect potassium levels should be cautious about consuming too much potassium-rich foods, including raisins.
Buying and Storing Tips
When buying black raisins, here are some tips to ensure you get good quality and store them properly:
Buying Tips:
- Check the Appearance: Look for black raisins that are plump, shiny, and free from wrinkles or mold. They should have a deep, dark color, indicating they were properly dried.
- Consider Organic Options: If possible, opt for organic black raisins to minimize exposure to pesticides and chemicals.
- Read the Label: Check the ingredients list to ensure there are no added sugars or preservatives if you prefer a more natural product.
- Buy from Reliable Sources: Purchase black raisins from reputable grocery stores, health food stores, or online retailers known for quality dried fruits.
Storing Tips:
- Store in a Cool, Dry Place: Transfer black raisins to an airtight container or resealable bag and store them in a cool, dry pantry. Avoid exposure to heat and moisture to prevent them from becoming sticky or molding.
- Avoid Refrigeration: While some suggest refrigerating raisins to extend their shelf life, this can cause them to absorb moisture and lose their texture. It’s generally best to store them at room temperature.
- Use Proper Containers: Airtight containers or resealable bags help maintain freshness and prevent the raisins from drying out or absorbing odors from other foods.
- Check for Freshness: Periodically check stored raisins for any signs of mold or off odor. If properly stored, they should remain fresh for several months to a year.
- Consider Freezing (optional): If you want to extend shelf life further, you can freeze black raisins in an airtight container. They will keep well for up to a year in the freezer, but allow them to come to room temperature before using.
Economic and Social Impact
The production and consumption of black raisins have significant economic and social impacts, both locally and globally. Here’s an overview of these impacts:
Economic Impact:
- Employment: The cultivation of grapes for raisin production provides employment opportunities for agricultural workers, ranging from planting and cultivating grapes to harvesting and processing raisins. This contributes to rural livelihoods in many regions where grape cultivation is a significant industry.
- Export Industry: Countries that are major producers of raisins, such as Turkey, Iran, the United States (particularly California), Greece, and Australia, rely on raisin exports as a source of revenue. The global demand for raisins, including black raisins, drives agricultural production and trade in these regions.
- Value Chain: The raisin industry supports a complex value chain involving farmers, processors, distributors, and exporters. This creates economic interdependencies and business opportunities for various stakeholders, including logistics and packaging industries.
- Market Stability: Raisin production can provide stability to agricultural economies by diversifying crop choices and providing a market for surplus grapes that may not be suitable for fresh consumption.
- Income Generation: For small-scale farmers, cultivating grapes for raisins can be a profitable venture, especially when integrated into diversified farming systems that include other crops or livestock.
Social Impact:
- Cultural Importance: In regions where grape cultivation and raisin production are traditional practices, such as in parts of the Mediterranean and Middle East, raisins hold cultural significance. They are used in traditional dishes, festivals, and celebrations, preserving cultural heritage and culinary traditions.
- Community Development: The raisin industry can contribute to community development through infrastructure improvements, education, healthcare, and other social programs funded by revenue generated from agricultural activities.
- Nutritional Security: Raisins, including black raisins, are a source of essential nutrients and energy, particularly in regions where access to fresh fruits may be limited. They contribute to nutritional security and food diversity in diets.
- Environmental Impact: Sustainable grape cultivation practices for raisin production, such as water management and soil conservation, can have positive environmental impacts by promoting biodiversity and reducing ecological footprint.
- Gender Empowerment: In some regions, grape cultivation and raisin production provide opportunities for women to participate in agricultural activities and generate income, contributing to gender empowerment and economic parity.

FAQ (frequently asked questions)
1. What are black raisins? Black raisins are dried grapes with a dark color, ranging from dark brown to almost black. They are made by drying specific grape varieties, such as Black Corinth or Black Muscat.
2. What are the health benefits of black raisins? Black raisins are rich in antioxidants, fiber, and essential vitamins and minerals like potassium and iron. They can support heart health, aid digestion, provide natural energy, and contribute to overall well-being.
3. How should black raisins be stored? Black raisins should be stored in a cool, dry place in an airtight container or resealable bag. Avoid refrigeration as it can cause them to absorb moisture and lose texture.
4. How can black raisins be used in cooking? Black raisins are versatile and can be used in baking (cakes, cookies, breads), salads, rice dishes, curries, trail mixes, and desserts (puddings, pies). They add sweetness, texture, and flavor to various dishes.
5. Are there any potential disadvantages of consuming black raisins? While nutritious, black raisins are calorie-dense due to their natural sugars and can contribute to weight gain if consumed excessively. They may also cause dental issues if not followed by proper oral hygiene due to their sticky texture.
6. Can individuals with diabetes consume black raisins? Individuals with diabetes should consume black raisins in moderation due to their natural sugar content. It’s important to monitor portion sizes and consider their overall carbohydrate intake.
7. Are there any allergens in black raisins? Some black raisins may contain sulfites as preservatives, which can cause allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. It’s advisable to check labels if you have sulfite sensitivity.
8. How long do black raisins last? When stored properly in a cool, dry place, black raisins can remain fresh for several months to a year. Checking them periodically for signs of mold or off odor is recommended.
Conclusion
Black raisins are not just a delicious addition to your pantry but also a powerhouse of nutrients that can benefit your overall health. Whether eaten on their own, added to dishes, or used in baking, these little jewels provide a natural sweetness and a wealth of health-promoting properties. Incorporating black raisins into your diet can be a simple and enjoyable way to boost your nutrition and enhance your well-being.
Table of Contents
Read more about Black raisins
Go and visit dusearchit.in and get more knowledge about others topics.
