What is Amla Juice?

Amla juice is a beverage made from the fruit of the amla tree, also known as the Indian gooseberry (Phyllanthus emblica). The amla fruit is highly valued in traditional Indian medicine, particularly in Ayurveda, for its health benefits.
Amla juice is often consumed for its high vitamin C content and antioxidant properties. It’s believed to help boost the immune system, improve digestion, enhance skin health, and provide overall wellness benefits. The juice can be quite tart due to the natural acidity of the amla fruit, and it’s sometimes sweetened or mixed with other juices to make it more palatable.
History & Origin
The origin of amla juice traces back to the amla fruit (Phyllanthus emblica), which is native to the Indian subcontinent. Here’s a more detailed look at its origin:
Botanical and Geographic Origin:
- Native Habitat: The amla tree is indigenous to India, as well as parts of Southeast Asia including Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Myanmar, and Thailand. It thrives in tropical and subtropical climates.
- Historical Cultivation: The amla fruit has been cultivated in India for thousands of years. It is integral to the natural landscape of the region and has been used extensively in traditional medicine and culinary practices.
Historical and Cultural Context:
- Ayurvedic Medicine: The fruit has been a cornerstone of Ayurveda, the ancient system of medicine that developed in India over 5,000 years ago. Ayurveda employs the amla fruit for its health-promoting properties, and it is featured in many classical Ayurvedic texts.
- Ancient Texts: References to amla can be found in ancient Indian texts such as the Charaka Samhita and the Sushruta Samhita. These texts describe the fruit’s medicinal benefits and its role in various health treatments.
- Cultural Significance: Beyond its medicinal uses, the amla tree is also revered in Indian culture. It is sometimes associated with longevity and health, and its fruit is used in traditional religious rituals.
Evolution to Modern Use:
- Global Spread: While its origins are firmly rooted in India, the use of amla has spread globally. Modern health and wellness trends have brought amla juice and other amla products to a wider audience, extending its use beyond traditional practices.
- Commercial Production: Today, amla juice is commercially produced and available in various forms worldwide, reflecting its enduring popularity and recognized health benefits.
Cultivation & harvesting
The cultivation of the amla tree (Phyllanthus emblica) involves several key practices to ensure healthy growth and high-quality fruit production. Here’s a detailed look at how amla is cultivated:

Growing Conditions:
- Climate: Amla trees thrive in tropical and subtropical climates. They can withstand mild drought and like warm weather. They grow well in regions with annual rainfall ranging from 500 to 1,500 mm.
- Soil: The trees are adaptable to a variety of soil types but perform best in well-drained, sandy loam soils. They can also grow in poor or rocky soils but require good drainage to prevent root rot.
- Elevation: Amla trees are typically grown at altitudes ranging from sea level up to 1,500 meters.
Planting:
- Propagation: Amla trees can be propagated from seeds or cuttings. Seed propagation is common, though it may take a bit longer for the trees to start bearing fruit. Vegetative propagation through cuttings or grafting is used to produce more uniform and faster-producing trees.
- Spacing: When planting, space the trees about 6 to 8 meters apart to allow for their spread and to ensure adequate air circulation.
Care and Maintenance:
- Watering: Regular watering is important, especially during the dry season. However, the trees are relatively drought-resistant once established.
- Fertilization: Amla trees benefit from periodic fertilization with organic compost or well-balanced fertilizers. This helps in maintaining soil fertility and supporting healthy growth.
- Pruning: Pruning is necessary to maintain the shape of the tree, remove dead or diseased branches, and improve air circulation. It can also help in managing the size of the tree for easier harvesting.
- Pest and Disease Management: Common pests include fruit flies and scale insects. Regular monitoring and integrated pest management practices help control these issues. Diseases like fungal infections may also affect the trees, and proper sanitation and treatment with fungicides may be required.
Harvesting:
- Timing: Amla fruits are typically harvested from November to March, depending on the local climate and variety. They are usually picked when they are mature but still firm.
- Methods: The fruits are generally harvested by hand. Care is taken to avoid damaging the fruit or the tree during the process.
Post-Harvest:
- Processing: Once harvested, the amla fruit can be used fresh or processed into various products such as amla juice, dried amla, or amla powder. Processing methods vary depending on the intended use.
- Storage: Fresh amla fruits have a short shelf life and are best used promptly or processed for longer-term storage.
Recipe
It’s easy to make amla juice at home, and it guarantees that you get the maximum amount of nutrients without any added chemicals or preservatives. Here’s a detailed how-to:
Components:
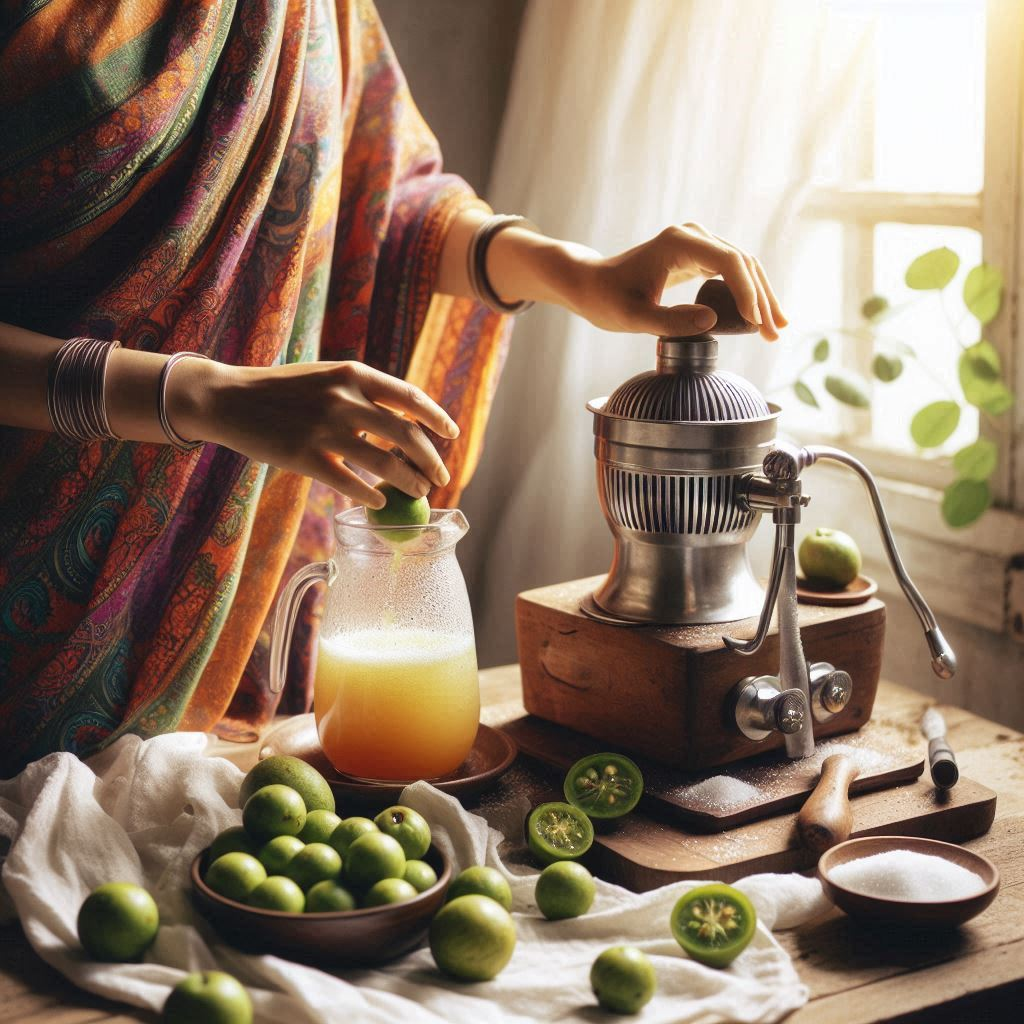

Amla berries in season (8–10)
Two cups of water
Optionally added jaggery or honey for sweetness
Getting ready: Thoroughly wash the amla berries to get rid of any dirt or contaminants.
Remove the seeds and chop the berries into small pieces.
Place the amla chunks in a blender with water and blend until smooth.
To remove the juice, strain the mixture through cheesecloth or a fine mesh strainer.
If you want to sweeten the juice, you can add jaggery or honey. Mix thoroughly.
Keep in mind:
Fresh amla juice should be refrigerated in an airtight container. To preserve its nutritious worth, it should be eaten within two to three days.
Nutritional composition
Amla (Indian gooseberry) is renowned for its exceptional nutritional profile and health benefits. Here’s a detailed look at the nutritional composition of amla, particularly focusing on the fruit:
Nutritional Composition (Per 100 grams of Fresh Amla):
- Calories: Approximately 44 kcal
- Water Content: About 90%
- Carbohydrates: Around 10 grams
- Sugars: 3-4 grams (includes natural sugars like glucose and fructose)
- Dietary Fiber: 2.4 grams
- Protein: 0.9 grams
- Fats: 0.1 grams
- Saturated Fat: Minimal
- Vitamins:
- Vitamin C: Approximately 600-700 mg (varies with ripeness; significantly high compared to other fruits)
- Vitamin A: Small amounts
- Vitamin B Complex: Includes B1 (thiamine), B2 (riboflavin), B3 (niacin), and B5 (pantothenic acid) in minor amounts
- Minerals:
- Calcium: 25-30 mg
- Iron: 0.6-0.8 mg
- Phosphorus: 27 mg
- Potassium: 150-200 mg
- Magnesium: 10 mg
- Sodium: Very low
- Antioxidants:
- Phenolic Compounds: Such as gallic acid, ellagic acid, and tannins
- Flavonoids: Including quercetin and kaempferol
- Other Antioxidants: Contribute to its high antioxidant activity
Culinary uses
Amla (Indian gooseberry) is a versatile fruit used in a variety of culinary applications, particularly in Indian and Southeast Asian cuisines. Here’s a rundown of how amla is used in cooking and food preparation:
1. Fresh Amla
- Raw Consumption: While the raw amla fruit is quite tart and sour, it can be eaten fresh. Often, it is sliced and sprinkled with salt or mixed with other fruits to balance its tartness.
- Salads: Fresh amla can be added to salads for a tangy flavor. It’s commonly used in Indian salads, sometimes combined with other vegetables and spices.
2. Pickles
- Amla Pickle: A traditional Indian preparation, amla pickle is made by preserving the fruit with spices, salt, and sometimes oil. It’s a popular accompaniment to meals, adding a spicy and tangy flavor.
3. Chutneys and Relishes
- Amla Chutney: Amla can be used to make chutneys or relishes. It is often combined with ingredients like green chilies, ginger, and spices to create a tangy and spicy condiment.
4. Juices and Beverages
- Amla Juice: Extracted from the fruit, amla juice is consumed for its health benefits. It is often mixed with other juices or sweetened to make it more palatable.
- Smoothies: Amla powder or juice can be added to smoothies for a boost of nutrients and flavor.
5. Dried and Powdered Amla
- Amla Powder: Made from dried amla, this powder is used as a dietary supplement or ingredient in various recipes. It can be added to teas, smoothies, or used in baking.
- Herbal Teas: Amla powder or dried amla can be steeped to make herbal teas that are enjoyed for their health benefits.
6. Cooking and Baking
- Curries and Stews: Amla can be used in curries and stews to add a tangy flavor. It’s often combined with other ingredients and spices to complement its sour taste.
- Baked Goods: Amla powder or extracts can be incorporated into baked goods like muffins or cakes for added nutritional value.
7. Traditional Sweets and Desserts
- Amla Candy: In some regions, amla is preserved in sugar to make a sweet, chewy candy known as “amla murabba.”
- Desserts: Amla can be used in traditional desserts, often paired with sweeteners to balance its sourness.
8. Traditional and Regional Dishes
- Amla Rice: In some Indian recipes, amla is cooked with rice and spices to create a tangy rice dish.
- Amla Raita: This is a yogurt-based dish where amla is mixed with yogurt and spices, similar to a cucumber raita.
Tips for Using Amla in Cooking
- Balancing Flavors: Amla’s tartness can be intense, so it’s often balanced with sweeteners or combined with other ingredients to create a harmonious flavor profile.
- Preservation: Fresh amla has a short shelf life, so it’s often preserved through drying or pickling to extend its usability.
Benefits
1. Immune System Support
- High Vitamin C Content: Amla is exceptionally rich in vitamin C, which is crucial for a robust immune system. Vitamin C helps stimulate the production of white blood cells, which are vital for fighting infections and diseases.
2. Antioxidant Properties
- Rich in Antioxidants: Amla contains powerful antioxidants like vitamin C, flavonoids, and polyphenols. By scavenging free radicals, these antioxidants lessen oxidative stress and the chance of developing chronic illnesses.
3. Digestive Health
- High Fiber Content: Amla is a good source of dietary fiber, which aids digestion by promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation.
- Digestive Aid: Amla can help soothe the digestive tract, improve appetite, and support overall digestive health.
4. Skin Health
- Anti-Aging: The antioxidants in amla help protect the skin from oxidative damage and premature aging. Vitamin C also supports collagen production, which is essential for skin elasticity and youthfulness.
- Skin Conditions: Amla is sometimes used in topical preparations to treat skin conditions and enhance skin health.
5. Hair Health
- Hair Growth: Amla is believed to promote hair growth and strengthen hair follicles. It is commonly used in hair oils and shampoos to improve hair health and reduce hair loss.
- Dandruff Control: The antimicrobial properties of amla can help in controlling dandruff and other scalp issues.
6. Cardiovascular Health
- Heart Health: The antioxidants and vitamin C in amla help protect against cardiovascular diseases by reducing cholesterol levels, preventing oxidation of LDL cholesterol, and improving overall heart health.
7. Blood Sugar Regulation
- Glycemic Control: Some studies suggest that amla can help in managing blood sugar levels and improving insulin sensitivity, making it beneficial for people with diabetes.
8. Weight Management
- Metabolism Boost: Amla may support metabolism and aid in weight management by helping to regulate appetite and improve digestion.
9. Liver Health
- Detoxification: Amla supports liver function and detoxification processes. Its antioxidant properties help protect the liver from damage caused by toxins and oxidative stress.
10. Respiratory Health
- Cough and Cold Relief: The anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties of amla can help in alleviating symptoms of respiratory conditions such as coughs and colds.
11. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
- Reduction of Inflammation: Amla’s anti-inflammatory compounds can help reduce inflammation in the body, which is beneficial for managing inflammatory conditions.
12. Bone Health
- Calcium and Phosphorus: Amla contains essential minerals like calcium and phosphorus, which are important for maintaining bone health and preventing osteoporosis.
Traditional and Complementary Uses
- Ayurvedic Medicine: In Ayurveda, amla is used as a key component in various formulations for its overall health benefits. It is included in products aimed at rejuvenation, detoxification, and balancing bodily doshas.
Usage and Consumption Tips
- Fresh and Dried Forms: Amla can be consumed fresh, dried, or in powdered form. Each form offers different benefits and uses in cooking and health supplements.
- Moderation: While amla is highly beneficial, it’s best consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet to avoid any potential side effects or interactions with other medications.
Disadvantages
While amla (Indian gooseberry) offers numerous health benefits, there are also some potential disadvantages and considerations to be aware of. Here’s a look at the possible drawbacks and side effects of consuming amla:
1. Gastrointestinal Issues
- Acidity and Heartburn: Due to its high vitamin C and acidity, consuming large amounts of amla may cause gastrointestinal discomfort, such as acidity or heartburn, especially in sensitive individuals.
- Digestive Disturbances: In some cases, excessive consumption of amla might lead to digestive issues such as diarrhea or stomach cramps.
2. Allergic Reactions
- Allergic Reactions: Although rare, some individuals may experience allergic reactions to amla, which could include symptoms like itching, swelling, or rashes. If you have a known allergy to amla or related fruits, it’s best to avoid it.
3. Interaction with Medications
- Blood Sugar Medications: Amla may lower blood sugar levels, which can interact with medications used to manage diabetes. It’s important for individuals on blood sugar-lowering medications to monitor their blood sugar levels closely if consuming amla regularly.
- Anticoagulants: Amla might affect blood clotting, so it could interact with anticoagulant or antiplatelet medications. This might increase the risk of bleeding or interfere with medication efficacy.
4. Iron Absorption
- Iron Absorption: The high vitamin C content in amla enhances iron absorption, which is generally beneficial. However, if you have conditions like hemochromatosis (a condition where the body absorbs too much iron), excessive consumption of amla might exacerbate iron overload.
5. Overconsumption Concerns
- High Vitamin C Levels: Excessive intake of amla, particularly in supplement form, can lead to an overload of vitamin C, potentially causing kidney stones or gastrointestinal discomfort.
- Potential for Overuse: Like any supplement or medicinal food, amla should be consumed in moderation. Overuse may lead to potential side effects, and it’s important to balance its intake with other dietary components.
6. Quality and Purity Issues
- Contaminants in Supplements: Some amla supplements or processed products may contain added sugars, preservatives, or contaminants. It’s essential to choose high-quality products from reputable sources to avoid potential adverse effects.
7. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
- Limited Research: There is limited research on the safety of amla during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult a healthcare provider before including amla in their diet, especially in supplement form.
8. Individual Sensitivities
- Personal Sensitivity: Each person’s tolerance to amla may vary. While many people can consume amla without issues, others may experience discomfort or adverse effects depending on their individual health conditions and sensitivities.
Recommendations for Safe Consumption
Quality Control: Choose high-quality, pure amla products to avoid contaminants and added substances that might cause adverse effects.
Moderation: Consume amla in moderation as part of a balanced diet. Start with tiny doses and see how your body reacts.
Consult Healthcare Providers: If you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications, consult a healthcare provider before adding significant amounts of amla to your diet or starting supplements.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ’s)
1. What is amla juice? Amla juice is a beverage made from the extract of amla (Indian gooseberry) fruit. It is well-known for both its numerous health advantages and high vitamin C content.
2. How is amla juice made? Amla juice is made by extracting the juice from fresh amla fruits, which can be done through blending, pressing, or using a juicer. The juice may be consumed fresh or processed for longer shelf life.
3. What does amla juice taste like? Amla juice has a tart, tangy, and slightly bitter taste due to the natural acidity of the fruit. It is often mixed with other juices or sweeteners to make it more palatable.
4. What are the health benefits of drinking amla juice? Amla juice offers numerous health benefits, including boosting the immune system, providing antioxidants, aiding digestion, improving skin health, promoting hair growth, and supporting overall wellness.
5. How does amla juice support immune health? The high vitamin C content in amla juice helps strengthen the immune system by stimulating the production of white blood cells, which are crucial for fighting infections.
6. Can amla juice help with digestion? Yes, amla juice can aid digestion due to its high fiber content and its ability to stimulate digestive enzymes. It can help improve digestion and relieve constipation.
7. How much amla juice should I drink daily? It is generally recommended to drink about 20-30 ml of amla juice daily. It’s best to start with a smaller amount to see how your body responds and adjust as needed.
8. When is the best time to drink amla juice? Amla juice can be consumed on an empty stomach in the morning for optimal absorption, or at any time of the day. Some people prefer to mix it with other juices or water.
9. Can I mix amla juice with other beverages? Yes, amla juice can be mixed with other fruit juices, such as orange or apple juice, to improve its taste. It can also be put to smoothies or diluted with water.
10. Are there any side effects of drinking amla juice? While amla juice is generally safe for most people, consuming it in excess can lead to gastrointestinal discomfort, such as acidity or diarrhea. It is recommended to use it sparingly.
11. Can amla juice interact with medications? Amla juice may interact with certain medications, particularly those for diabetes or blood thinning. It’s important to consult a healthcare provider if you are on medication before consuming amla juice regularly.
12. Is amla juice safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding? There is limited research on the safety of amla juice during pregnancy and breastfeeding. It’s advisable to consult a healthcare provider before consuming amla juice during these periods.
13. How should I choose high-quality amla juice? Choose amla juice that is made from 100% pure amla with minimal added sugars or preservatives. Check for certifications and opt for reputable brands to ensure quality and purity.
14. Can I make amla juice at home? Yes, you can make amla juice at home by blending fresh amla fruits and straining the mixture to extract the juice. Ensure you use clean, fresh amla and follow proper hygiene practices.
15. How long does amla juice last? Freshly made amla juice should be consumed within a few days if stored in the refrigerator. Commercially processed amla juice typically has a longer shelf life, but always check the expiration date and storage instructions on the label.
Conclusion
Amla juice is a remarkable health tonic with a wide range of benefits that align with both traditional and modern health practices. Its high vitamin C content, antioxidant properties, and overall nutritional profile make it a valuable addition to your daily routine. Whether you’re looking to boost your immune system, improve your skin, or support heart health, amla juice offers a natural and effective solution.
Table of Contents
Read more about Amla juice
Go and visit dusearchit.in and get more knowledge about others topics.
