What is Pista?
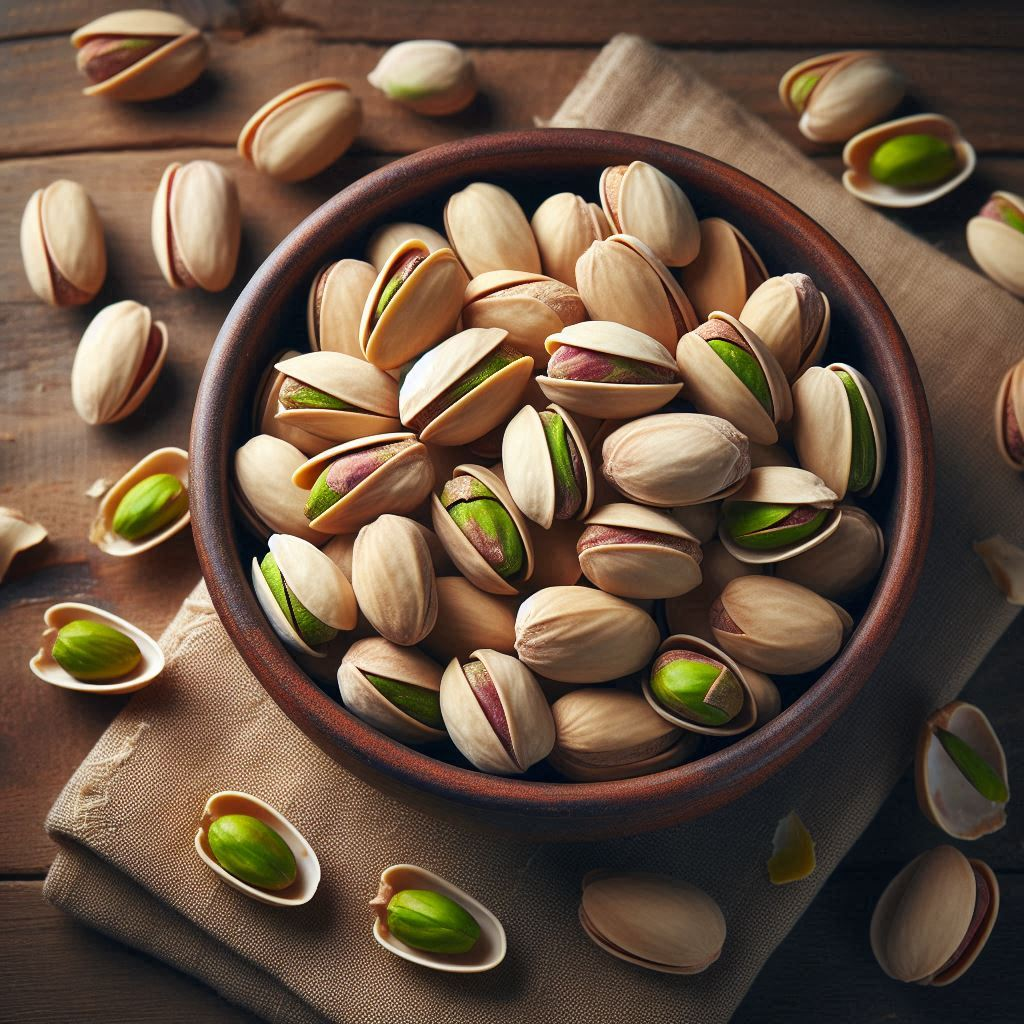

Pista are nuts that come from the pistachio tree (Pistacia vera). They have a hard, beige shell that encloses the edible seed, which is green and yellow in color.
Pistac are frequently used in baking and cooking, or consumed as a snack. They have a slightly sweet and nutty flavor, and are known for their distinct greenish coloration and their use in both sweet and savory dishes worldwide
Origin & cultivation
Pista have a long history dating back thousands of years and are believed to have originated in the regions of Central Asia and the Middle East, particularly Iran, where they have been cultivated for millennia. They were introduced to the Mediterranean region, including Greece and Italy, by traders and travelers around 1st century AD.
Cultivation of pista requires a warm climate with hot summers and cool winters, as they thrive in regions with a long, dry growing season. They are primarily grown in countries such as Iran, the United States (particularly California), Turkey, Syria, and Greece. The trees are relatively hardy and drought-resistant once established, but they do require well-drained soil and good sunlight for optimal growth.

Pista trees typically begin producing nuts after about five to seven years, with peak production occurring between 15 to 20 years of age. The nuts grow in clusters similar to grapes and have a harvest season that typically starts in late summer to early autumn, depending on the region. Harvesting is usually done by shaking the branches or by using mechanical shakers to dislodge the ripe nuts from the trees.
Types
There are several main types or varieties of pista that are commercially grown and recognized:
- Kerman: This is the most widely grown variety worldwide, particularly in Iran and California (USA). It has large, elongated nuts with a distinctive shape and vibrant green color.
- Akbari: Also known as “Long” pistachios, these are grown primarily in Iran. They are known for their long, slender shape and are prized for their rich flavor and excellent shell split.
- Ahmad Aghaei: Another Iranian variety, Ahmad Aghaei pistachios are known for their slightly smaller size compared to Kerman and Akbari. They have a deep green kernel and are popular for snacking and culinary uses.
- Round: This type includes varieties like Kalehghouchi from Iran and Fiesta from California. Round pistachios have a more spherical shape compared to the elongated types and are often used in confectionery and as ingredients in various dishes.
- Siirt: Originating from Turkey, Siirt pistachios are known for their small size and excellent flavor. They are often used in traditional Turkish desserts and snacks.
- Antep: Also known as Gaziantep pistachios, these are grown in Turkey and are famous for their rich, nutty flavor and vibrant green color. They are a key ingredient in Turkish cuisine and desserts.
Growing regions in India
Pista are primarily grown in specific regions of India where the climate and soil conditions are suitable for their cultivation. The main states where pista are grown in India include:

- Jammu and Kashmir: This region, particularly in districts like Pulwama and Anantnag, is known for its pistachio cultivation. The climate and altitude in parts of Jammu and Kashmir are favorable for growing high-quality pistachios.
- Himachal Pradesh: Some areas in Himachal Pradesh, especially in the Kangra district and other hill regions, also cultivate pistachios. The cool climate in these regions supports the growth of pistachio trees.
- Uttarakhand: Parts of Uttarakhand, such as the hilly regions around Nainital and Almora, have suitable conditions for pistachio cultivation. Farmers in these areas have started growing pistachios as an alternative crop.
- Arunachal Pradesh: In the northeastern state of Arunachal Pradesh, particularly in regions with similar climatic conditions to Jammu and Kashmir, pistachio cultivation has been experimented with and shows potential.
Composition
Pistachios are nutrient-dense nuts that provide a variety of essential vitamins, minerals, and other beneficial compounds per serving (about 28 grams or 1 ounce):
- Calories: Approximately 156 calories, making them a relatively calorie-dense food.
- Protein: About 6 grams of protein, which is relatively high compared to other nuts.
- Fat: Around 12 grams of fat, predominantly healthy monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, with a low amount of saturated fat.
- Carbohydrates: Approximately 8 grams of carbohydrates, including 3 grams of fiber.
- Vitamins:
- Vitamin B6: Important for brain function, metabolism, and immune system health.
- Vitamin E: Antioxidant vitamin E aids in preventing cell damage.
- Minerals:
- Potassium: Essential for heart health, muscle function, and blood pressure regulation.
- Phosphorus: Vital for the health of bones and the metabolism of energy.
- Magnesium: Supports nerve and muscle function, immune system health, and bone strength.
- Iron: Helps transport oxygen throughout the body.
- Antioxidants:
- Lutein and Zeaxanthin: Carotenoids that promote eye health and protect against age-related macular degeneration.
- Polyphenols: Plant compounds with antioxidant properties that help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation.
- Other Nutrients:
- Pistachios also contain small amounts of zinc, copper, manganese, and selenium, which are essential trace minerals important for various physiological processes.
benefits
Pistachios offer a range of nutritional benefits, making them a popular choice among nuts:
- Rich in Nutrients: Pistachios are packed with essential nutrients such as vitamins (vitamin B6, vitamin E), minerals (potassium, phosphorus, magnesium, iron), and antioxidants (such as lutein and zeaxanthin).
- Healthy Fats: They are relatively high in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which are beneficial for heart health when consumed in moderation.
- Protein: Pistachios provide a good amount of protein compared to other nuts, making them a satisfying snack that can help keep you full.
- Fiber: They are a good source of dietary fiber, which is important for digestive health and can help with managing blood sugar levels.
- Antioxidants: Pistachios contain antioxidants like carotenoids (lutein and zeaxanthin) and polyphenols, which help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals.
- Heart Health: Studies suggest that regular consumption of pistachios may help improve cholesterol levels by reducing LDL cholesterol (the “bad” cholesterol) and increasing HDL cholesterol (the “good” cholesterol).
- Weight Management: Despite being calorie-dense, pistachios may support weight management due to their protein, fiber, and healthy fat content, which can help promote feelings of fullness and reduce overall calorie intake.
- Blood Sugar Control: The fiber and healthy fats in pistachios may contribute to improved blood sugar control, particularly in individuals with diabetes.
Disadvantages
While pistachios offer numerous health benefits, there are a few potential disadvantages to consider:

- Caloric Density: Pistachios are calorie-dense, with approximately 156 calories per ounce (28 grams). Eating large quantities without moderation can contribute to weight gain, especially if not accounted for within daily caloric needs.
- Potential Allergies: Like other nuts, pistachios can cause allergic reactions in some individuals. Symptoms can range from mild itching or swelling to more severe reactions like difficulty breathing or anaphylaxis.
- High Fat Content: Although most of the fats in pistachios are healthy monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, they still contribute to the overall calorie content. Overconsumption may lead to an excessive intake of fats if not balanced with other nutrient-dense foods.
- Sodium Content: Some commercially available pistachios may be salted, which can increase sodium intake. High sodium consumption is linked to hypertension (high blood pressure) and other cardiovascular problems.
- Oxalates: Pistachios contain oxalates, which can contribute to the formation of kidney stones in susceptible individuals. Those with a history of kidney stones may need to moderate their intake of foods high in oxalates.
- Pesticide Residues: Depending on cultivation practices, pistachios may contain pesticide residues. Choosing organic pistachios or ensuring thorough washing can help reduce exposure to these chemicals.
- Potential Digestive Issues: Eating large quantities of pistachios, especially if not chewed thoroughly, can sometimes lead to digestive discomfort such as bloating, gas, or diarrhea due to their fiber content.
- Aflatoxin Risk: There is a slight risk of exposure to aflatoxins, naturally occurring toxins produced by certain molds that can grow on nuts like pistachios. This risk is generally low but can be minimized by purchasing high-quality, properly stored nuts.
Uses
Pistachios are incredibly versatile in the kitchen and are used in a wide range of culinary delights across various cuisines. Here are some delicious ways pistachios are enjoyed:
- Snacking: Pistachios are popularly enjoyed as a snack on their own, both raw or roasted and salted.
- Baking: Pistachios add a delightful crunch and nutty flavor to baked goods such as cookies, cakes, muffins, and biscotti. They can be chopped or ground and incorporated into the batter or used as a topping.
- Desserts: Pistachios are a key ingredient in many desserts around the world. They are commonly found in traditional Middle Eastern sweets like baklava, halva, and Turkish delight. In Western cuisine, they are used in ice creams, gelatos, pies, and tarts.
- Sauces and Dressings: Ground or finely chopped pistachios can be used to make flavorful sauces and dressings. They can be blended into pesto sauces, mixed into yogurt-based dressings, or used as a crunchy topping for salads.
- Middle Eastern and Mediterranean Dishes: Pistachios are a staple in Middle Eastern and Mediterranean cuisines. They are used in savory dishes such as pilafs, couscous, and stuffed vegetables. They also feature prominently in dishes like Persian rice dishes and Lebanese desserts.
- Nut Butters and Spreads: Pistachio butter, similar to almond or peanut butter, is a delicious alternative spread for toast, crackers, or as a dip for fruits and vegetables.
- Chocolate and Confections: Pistachios pair exceptionally well with chocolate. They are used in chocolate bars, truffles, and chocolate-covered nuts. They also add crunch and flavor to nougat, pralines, and other confections.
- Savory Applications: Pistachios can be used as a crust for fish or poultry, adding texture and flavor. They can also be sprinkled over salads, roasted vegetables, or pasta dishes for added crunch and richness.
- Nut Mixes: Pistachios are often included in mixed nuts and trail mixes, combining their unique flavor and texture with other nuts, seeds, and dried fruits.
- Drinks: Pistachio-flavored beverages, such as pistachio milk or pistachio liqueur, are popular in some cultures and can be enjoyed on their own or used as an ingredient in cocktails and mocktails.
Economic and Environmental Impact
The cultivation and consumption of pistachios have both economic and environmental impacts:
Economic Impact:
- Job Creation: Pistachio cultivation provides employment opportunities, particularly in regions where pistachios are a major agricultural crop, such as Iran, the United States (California), Turkey, and others. This includes jobs in farming, harvesting, processing, and distribution.
- Export Revenue: Pistachios are a valuable agricultural export commodity for producing countries. They contribute significantly to export earnings and foreign exchange reserves, particularly for countries like Iran and the United States, which are major exporters.
- Economic Growth: The pistachio industry supports local economies by generating income for farmers, processors, and other businesses involved in the supply chain. This can lead to overall economic growth and development in rural areas.
- Market Demand: There is a growing global demand for pistachios due to their nutritional benefits and culinary versatility. This sustained demand supports the economic viability of pistachio cultivation and trade.
Environmental Impact:
- Water Usage: Pistachio trees require substantial water for growth, particularly during the growing season. In regions with limited water resources or where water scarcity is a concern, pistachio cultivation can contribute to competition for water resources.
- Pesticide Use: Like other crops, pistachios may be treated with pesticides to control pests and diseases. The use of pesticides can have environmental implications, such as contamination of soil and water, as well as potential impacts on non-target organisms.
- Land Use and Habitat: Pistachio orchards require land for cultivation, which can lead to deforestation or conversion of natural habitats. Sustainable land management practices, such as agroforestry and biodiversity conservation, can mitigate these impacts.
- Soil Health: Intensive agricultural practices, including monoculture in pistachio cultivation, can affect soil health over time, leading to issues such as erosion, nutrient depletion, and loss of soil biodiversity. Practices such as crop rotation and soil conservation can help maintain soil fertility.
- Climate Change: Agriculture, including pista cultivation, contributes to greenhouse gas emissions through activities such as fertilizer use and machinery operation. However, pistachio trees themselves can act as carbon sinks, sequestering carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.

FAQ (frequently asked questions)
1. Are pista healthy?
- Yes, pista are nutritious. They are rich in protein, healthy fats (monounsaturated and polyunsaturated), fiber, vitamins (such as B vitamins and vitamin E), minerals (like potassium, phosphorus, and magnesium), and antioxidants.
2. How many calories are in pista?
- Approximately 156 calories per ounce (28 grams) of pista. This makes them a calorie-dense food, so portion control is important, especially if you’re watching your calorie intake.
3. Are pista good for weight loss?
- Despite being calorie-dense, pista can aid in weight loss due to their protein, fiber, and healthy fat content. They help keep you feeling full and satisfied, potentially reducing overall calorie intake when consumed in moderation.
4. Do pista help lower cholesterol?
- Yes, pista have been shown to help improve cholesterol levels by reducing LDL (bad) cholesterol and increasing HDL (good) cholesterol. This is due to their healthy fat content and other beneficial nutrients.
5. Are pista a good source of protein?
- Yes, pista provide about 6 grams of protein per ounce (28 grams). While they are not as high in protein as some other nuts like almonds or peanuts, they still contribute to your daily protein intake.
6. Can pista cause allergies?
- Yes, like other nuts, pista can cause allergic reactions in some individuals. From minor swelling or itching to more serious reactions like breathing difficulties or anaphylaxis, symptoms can vary widely. Nut allergies should steer clear of pistachios.
7. How should pista be stored?
- Pista should be stored in an airtight container in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. Alternatively, you can store them in the refrigerator or freezer to extend their shelf life. They retain their flavor and freshness longer when stored properly.
8. What are the different types of pista?
- There are several main varieties of pista, including Kerman, Akbari, Ahmad Aghaei, Round, Siirt, and Antep (Gaziantep). These varieties differ in size, shape, flavor profile, and where they are predominantly grown.
9. How are pista harvested?
- Pista are typically harvested by shaking the branches of the pista trees or using mechanical shakers to dislodge the ripe nuts. After harvesting, the nuts are processed to remove the outer hull and shell before being sold commercially.
10. What are some popular culinary uses of pista?
- Pista are used in a variety of culinary dishes and desserts around the world. They are commonly found in baklava, ice creams, salads, pesto sauces, and as a topping for yogurt or oatmeal. They also make a delicious snack on their own.
Conclusion
In conclusion, pista are more than just a delicious nut — they are a symbol of heritage, health, and culinary excellence. Pista are a popular food that have nourished people all over the world and captivated taste buds from their ancient origins. Whether enjoyed as a snack, an ingredient in gourmet cuisine, or a symbol of cultural tradition, pistachios are indeed nature’s green gold, enriching our lives in more ways than one. As we embrace a future of wellness and sustainability, pista stand tall as a shining example of how nature’s bounty can bring joy and nourishment to generations to come.
Table of Contents
Read more about Pista
Go and visit dusearchit.in and get more knowledge about others topics.
